Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy
Introduction
What is Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy?
Laparoscopic cholecystectomy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure to remove the gallbladder. The gallbladder is a small organ located under the liver, and it stores bile, a digestive fluid produced by the liver. This procedure is often recommended for individuals with gallstones or other gallbladder-related issues.
Why is it Done?
- Gallstones: Hardened deposits of digestive fluid that can cause pain, infection, or blockages.
- Cholecystitis: Inflammation of the gallbladder.
- Biliary Dyskinesia: Poor functioning of the gallbladder.
- Pancreatitis: Inflammation of the pancreas caused by gallstones.
Benefits of Laparoscopic Surgery
- Minimally Invasive: Small incisions mean less pain and quicker recovery.
- Faster Recovery: Most patients can go home the same day or the next day.
- Less Scarring: Smaller incisions result in less visible scars.
- Reduced Risk of Complications: Lower risk of infection and complications compared to open surgery.
How is the Procedure Done?
- Preparation: You’ll be given general anesthesia to put you to sleep during the surgery.
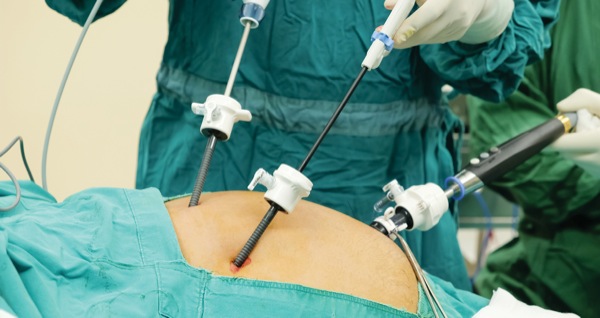
- Incisions: The surgeon makes a few small incisions in your abdomen.
- Insertion of Instruments: A tiny camera (laparoscope) and surgical instruments are inserted through the incisions.
- Removal of Gallbladder: The gallbladder is carefully detached and removed.
- Closing Incisions: The incisions are closed with sutures or staples.
What to Expect After Surgery
- Recovery Time: Most people return to normal activities within a week.
- Diet: You may need to follow a special diet for a few days.
- Pain Management: Mild pain or discomfort can be managed with over-the-counter pain relievers.
- Follow-Up: A follow-up appointment will be scheduled to check your recovery.
When to Contact Your Doctor
- Severe Pain: Uncontrolled pain that doesn’t improve with medication.
- Fever: A high fever may indicate an infection.
- Redness or Swelling: Around the incision sites, which could be a sign of infection.
- Digestive Issues: Persistent nausea, vomiting, or changes in bowel movements.
