Laparoscopic Appendicectomy
Introduction
What is a Laparoscopic Appendectomy?
A laparoscopic appendectomy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure to remove the appendix. It involves small incisions and the use of a camera to guide the surgery, making it a safer and faster option compared to traditional surgery.
Why is it Done?
The appendix is a small, tube-like organ attached to the large intestine. When it becomes inflamed or infected, a condition known as appendicitis, it needs to be removed to prevent complications. Symptoms of appendicitis include:
- Severe abdominal pain, especially on the right side
- Nausea and vomiting
- Fever
- Loss of appetite
Benefits of Laparoscopic Appendectomy
- Smaller Incisions: Only a few tiny cuts are made, leading to minimal scarring.
- Less Pain: Patients typically experience less postoperative pain.
- Faster Recovery: Most people can return to their normal activities sooner.
- Shorter Hospital Stay: Many patients go home the same day or within 24 hours.
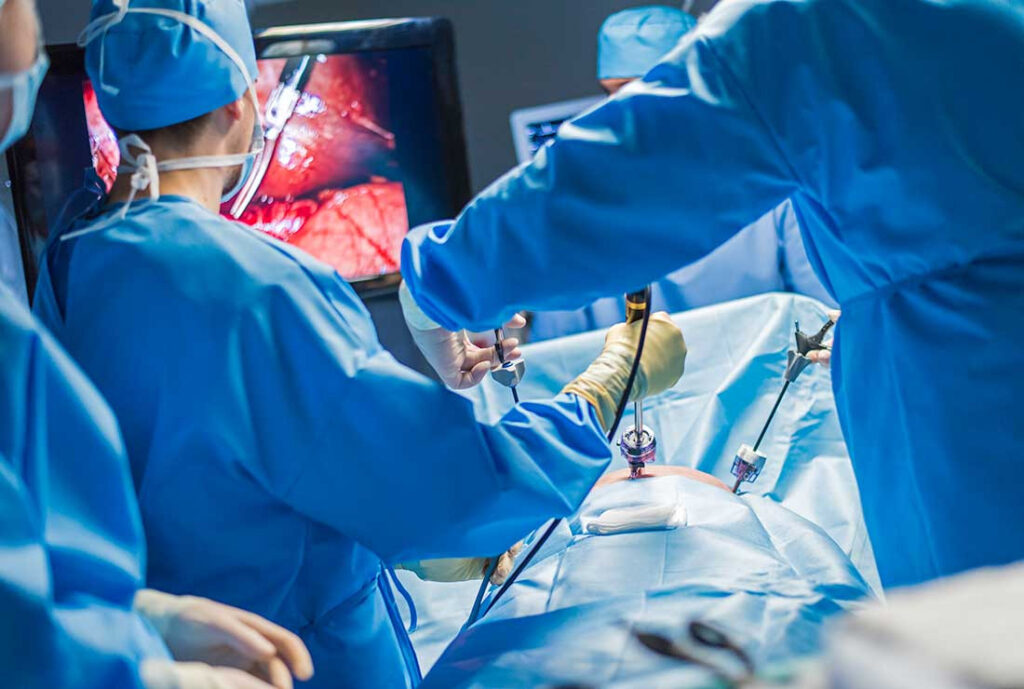
The Procedure
- Preparation: You will receive general anesthesia to ensure you are asleep and pain-free during the surgery.
- Incisions: Small incisions are made in the abdomen.
- Inserting the Camera: A laparoscope (a small camera) is inserted through one of the incisions. This camera sends images to a monitor, guiding the surgeon.
- Removing the Appendix: Surgical instruments are inserted through the other incisions to remove the appendix.
- Closing the Incisions: The small incisions are closed with stitches or surgical glue.
Recovery
- Post-Surgery: You may feel some discomfort around the incision sites, but this usually subsides quickly.
- Activity: Light activities can often be resumed within a few days. Strenuous activities should be avoided for a few weeks.
- Follow-Up: Dr. Sable will provide specific instructions and schedule a follow-up appointment to monitor your recovery.
